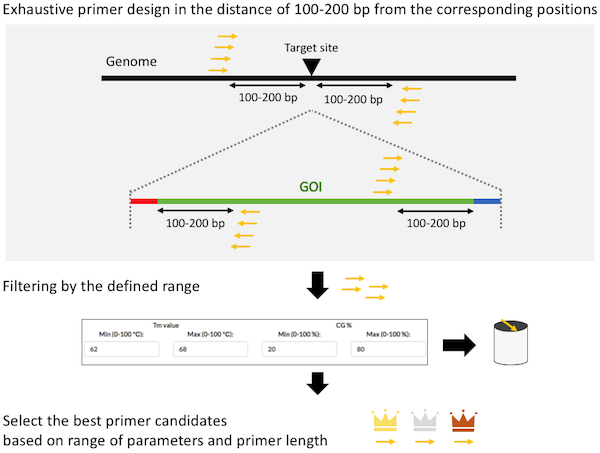
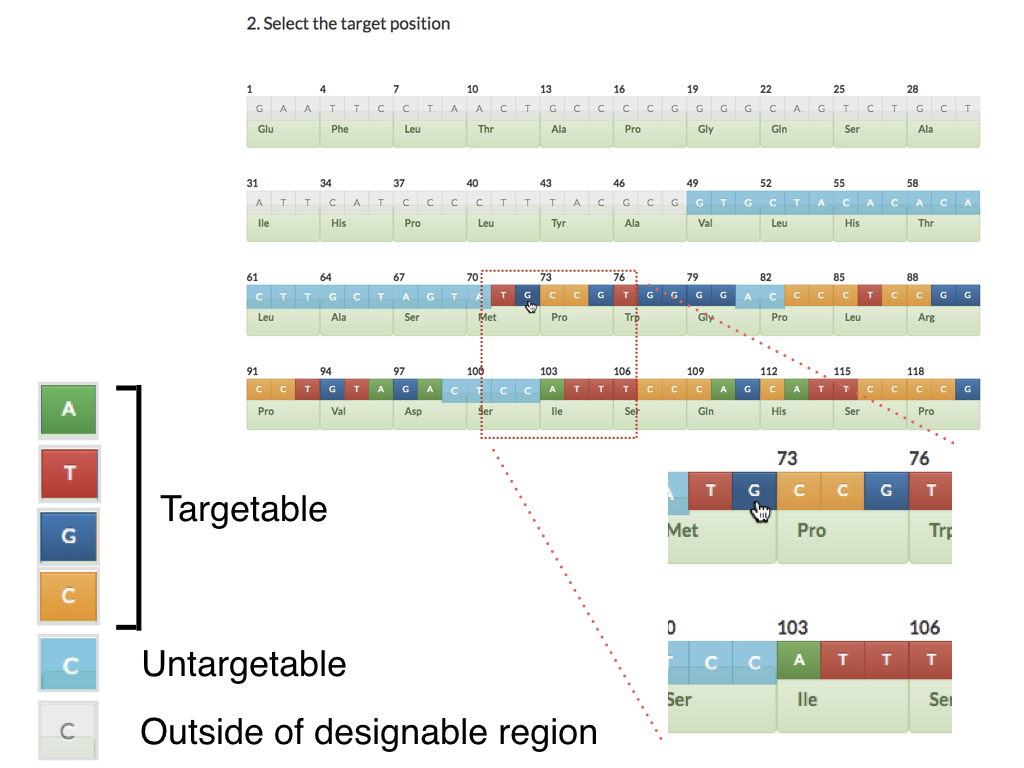
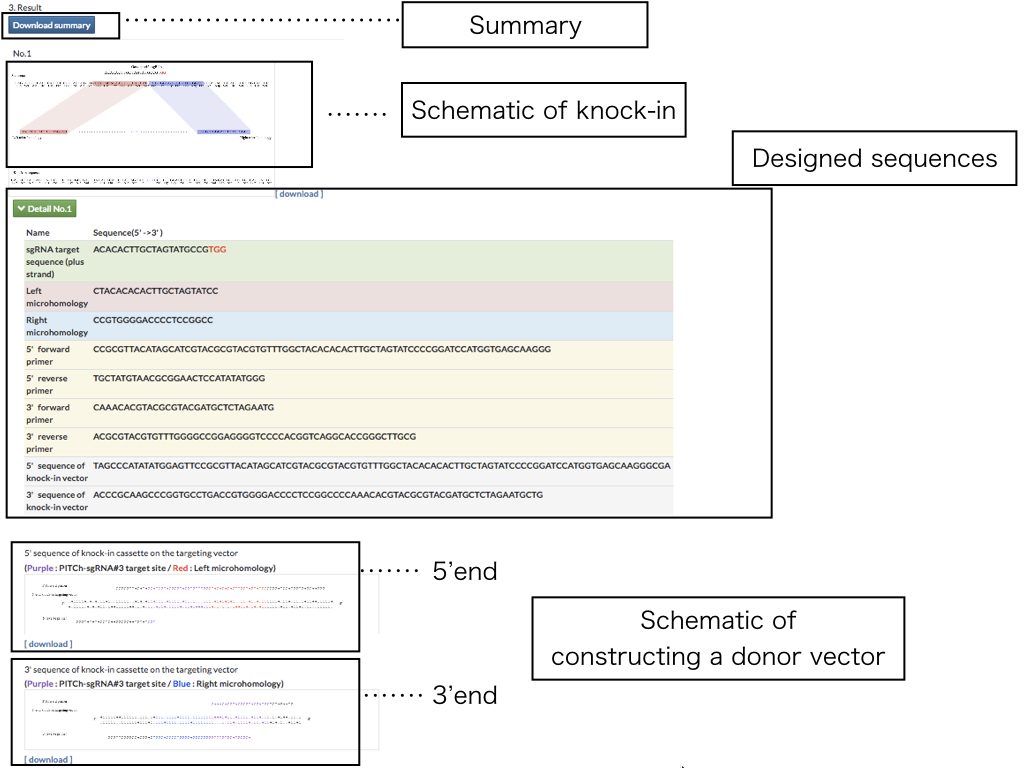
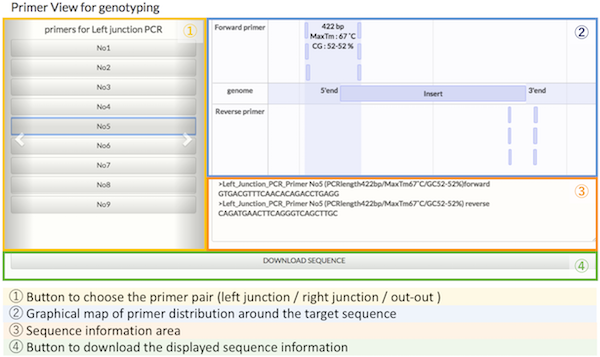
What are the PITCh systems ?
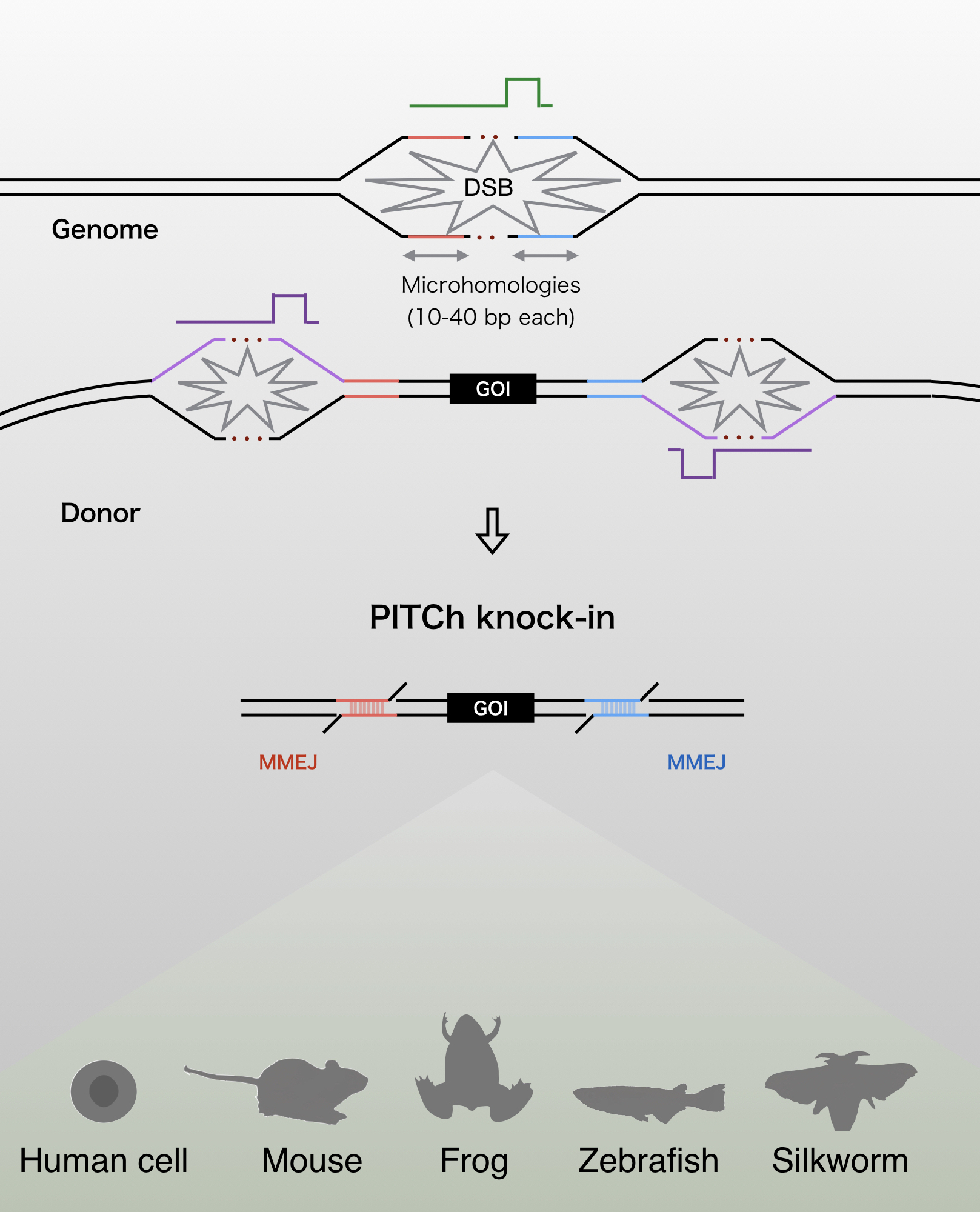
The PITCh (Precise Integration into Target Chromosome) systems are the alternative methods of CRISPR-Cas9- and TALEN-mediated knock-in
1
.
Advantages
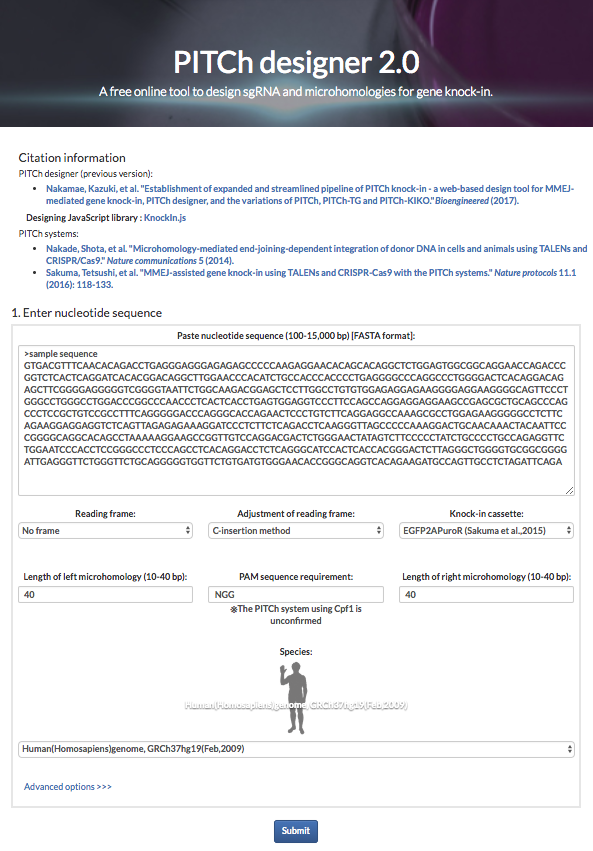
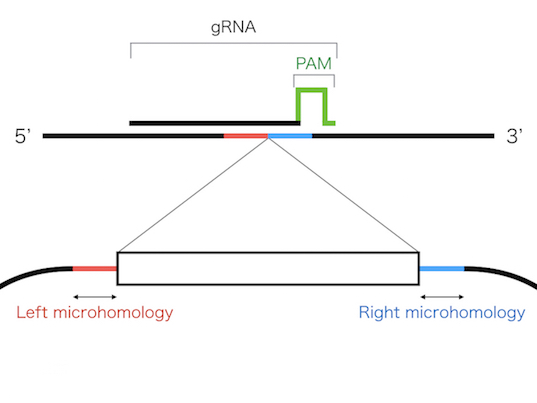
These systems enable seamless gene knock-in with extremely short homologous sequences (10–40 bp), which can be easily added to the donor vector by PCR and
In-Fusion cloning
1
.
The PITCh knock-in is based on one of the repair mechanism of DNA double strand break,microhomology-mediated end-joining (MMEJ). Since MMEJ is independent on homologous recombination
(HR), which is mainly used for gene knock-in, PITCh system can be utilized in cells and organisms with low HR frequency.
Applications
The PITCh systems have currently been applied in cultured cells (HEK293T, HeLa, HCT116, CHO), silkworms, frogs, zebrafish, and mice.